Summary
UML modeling, ‘name’ looks familiar! Yes, UML modeling used to represent object-oriented system, domain concepts, business requirement conceptual(analysis) model by architects/developers, domain experts, business analysts. UML modeling/diagram classified as class, object, use case, sequence, collaboration, statechart, activity, component, and deployment. I know you’re aware of classification :)
OMG provides a key foundation for Model-Driven Architecture®, which unifies every step of development and integration from business modeling, through architectural and application modeling, to development, deployment, maintenance, and evolution.
AndroMDA follows the Model Driven Architecture (MDA) paradigm. It takes model(s) from CASE-tool(s) and generates fully deployable applications and other components. AndroMDA uses Eclipse Modeling Framework (EMF) for Code Generation.
I will take you through profiles/stereotypes/things-to-know while doing UML modeling AndroMDA.
- Introduction of AndroMDA UML profiles
- Loading Downloaded UML profiles
- Modeling Entity & Data Access Object (DAO)
- Modeling Enumeration
- Modeling Value Object
- Modeling Generics – Collection, List, Set
- Modeling Optional and Mandatory Parameters
- Modeling Service
- Modeling REST & SOAP Web Service
- Modeling Dependency Injection
- Modeling Exception and Web Service Fault
- Sample AndroMDA Model & UML Diagram Download
I’m using MagicDraw UML product in this article. Currently this article does not cover jBPM & JSF related stereotypes, I’m planning create a dedicated article later.
Introduction of AndroMDA UML profile
AndroMDA provides various UML profiles for modeling; it helps to achieve Marked PIM to PSM while code generation.
- andromda-profile-datatype
- andromda-profile-messaging
- andromda-profile-meta
- andromda-profile-persistence
- andromda-profile-presentation
- andromda-profile-process
- andromda-profile-service
- andromda-profile-common
- andromda-profile-webservice
- andromda-profile-xml
Now, you may have question “How to get these profiles into my maven local repo?“; Its simple, follow this article “Java/J2EE project creation Using AndroMDA“. After completing Step 7 all the AndroMDA profiles will be in your Local Maven Repo ({path-your-maven-repo}/org/andromda/profiles/uml2).
Loading Downloaded UML profiles
Let’s begin UML modeling AndroMDA, open up the generated model file; model path as per above article.
Model location: ${base-directory}/andromdaapplication/mda/src/main/uml/andromdaapplication.xml
You will be presented with follow two environment variable value, provide this value. It will auto load all the AndroMDA UML profiles in the containment sidebar.
- maven2.repository: value is ‘path to your local maven repo’
- andromda3.root: value is ‘path to your local maven repo’
Note: I’m using MagicDraw UML 17.0.2 for illustration. Soon AndroMDA 3.4 Version will be pushed to Maven Central Repo.

Modeling Entity – Data Access Objects (DAO)
Entity we have to apply <<Entity>> stereotype and we have to apply few more annotation to UML Class. By default AndroMDA create the basic CRUD operations and few useful methods (load, loadAll, create, update, delete, findById, etc.) in the generated DAO class. Apply <<PersistentClass>> stereotype for hibernate XML generation.
Note: double click the class element, you will get dialog box; it provides option to configure below modeling properties.
- Database Table Name: mapping table name into UML class, we have to apply Tag andromda_persistence_table
- Database Table Column Name: for each attribute we have to apply Tag andromda_persistence_column
- Identifier (Primary Key): apply
<<Identifier>>stereotype to the primary key attribute - Composite Primary Key: apply
<<Unique>>stereotype to the attribute; secondary unique column of the table - Entity Association/Relationship: applying database table associations (table foreign key)
- User-Defined methods in {Entity}Impl Class or {DAO}Impl Class: by default UML operation considered as Entity methods/functions; if that method required to be DAO method/functions apply IsStatic property as true
- Database Operations cascade required: apply hibernate cascade option in the Tag andromda_persistence_cascade_type
- Enumeration: Java Enumeration fully supported in the Entity Class
- For Attributes: model all the attribute as Multiplicity value [0..1] and leave Identifier as mandatory attribute

Modeling Enumeration
Java5 type-safe enumerations are modeled by means of a regular class in UML, apply <<Enumeration>> stereotype to UML Class. Model all attributes with the default value property or AndroMDA will assume the name of the attribute if the default value is missing. This will generate your Java5 enum object containing your literals.
Note:
- Model all the attribute with public modifier or you will end up with model validations error/you enum will not get generate
- AndroMDA docs (Web Service cartridge Profile) states ‘Deprecated: Use UML Enumerations instead’. As of now I haven’t tried this one, will try soon :)

Modeling Value Object
Value Objects are typical used exchange information between methods/functions. Apply <<ValueObject>> stereotype in the UML Class.
- Mandatory Attributes: AndroMDA puts check at Service Level in the Base Class, if value not passed will throw exception
- Association: You can create association between ValueObject as required
- Transformation Methods: create a UML dependency between ValueObject and Entity; then AndroMDA creates transformation methods like Entity-To-ValueObject and ValueObject-To-Entity

Modeling Generics – Collections, List, & Set
Generics is easy in modeling; create a attribute, choose AndroMDA datatype or any ValueObject UML class and apply Multiplicity Property value –
- Choose 0..* or 1..*
- Collection: first bullet point & apply “Is Ordered & Is Unique” as false
- For List: first bullet point & apply “Is Ordered” property as true
- For Set: first bullet point & apply “Is Unique” property as true
Modeling Optional and Mandatory Parameters
You may feel this is kind side note but its important while modeling. Be it Service or Entity its plays a internal role for attributes. Default is mandatory, for optional attributes apply Multiplicity property value as [0..1].
- Value Object role at Service Layer: for mandatory attributes AndroMDA place null/empty check at {Service}Base class, if value is not present exception will be thrown
- Entity role at Data Access Layer: for mandatory attributes AndroMDA place null/empty check at {DAO}Base class, if value is not present exception will be thrown
Modeling Service
Presentation Layer, Inter application integration, Web Service producers consume service methods/functions and service methods have access to Business process management, Data access objects.
Apply <<Service>> stereotype to the UML Class element.

- DAO Access: Providing Service class access to DAO class, create a UML Dependency relationship in the class. Then AndroMDA creates Setter in the Service Class, those gets initialized through Spring IoC in the Application Context
- For Exception: apply “Raised Exception” property in the UML operation
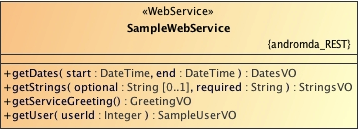
Modeling REST Web Service & SOAP Web Service
Web Service is another good part in the AndroMDA, easy to achieve in the application. There are two ways achieve Web Service implementation i.e. REST and SOAP –
- Expose all the methods as Web Service: Apply
<<WebService>>stereotype in the UML class - Expose selective methods as Web Service: Apply
<<WebServiceOperation>>stereotype in the UML operation - In the Web Service modeling you must Apply
<<XMLSchema>>stereotype to all the packages, it creates respective XSD - Default is SOAP Web Service in AndroMDA, can control whether SOAP 1.1 or 1.2 from ‘andromda.xml’ configuration
- For REST Web Services follow below pointers
- Apply
<<WebService>>stereotype in the UML class - To treat UML class as REST Web Service, so apply Tag ‘andromda_REST‘ value as true on UML class
- Following tag represents REST annotations for Service and Method
andromda_REST_path => @Path andromda_REST_produces => @Produces andromda_REST_consumes => @Consumes andromda_REST_provider => @Provider andromda_REST_request_type => @GET, @POST, @PUT, @DELETE, @HEADER, or @OPTIONS andromda_REST_http_method => @HttpMethod - Custom HTTP Method, other than GET/PUT/POST andromda_REST_contexts => @Context andromda_REST_encoded => @Encoded andromda_REST_retention => @Retention andromda_REST_target => @Target andromda_REST_suspend => @Suspend
- Following tag represents REST annotations for Method Parameter
andromda_REST_param_type => @PathParam, @QueryParam, @HttpHeader, @FormParam, @CookieParam, or @MatrixParam
andromda_REST_parameter_URL => /parameterurl/
andromda_REST_path_param => "userid" - used within param_type
andromda_REST_path_segment => "/{mapvalue:(.)+}" - A sequence of identically named parameters (queries, headers, etc) can be mapped to List or Set or SortedSet
Articles around Web Services using AndroMDA, have a look:
- “SOAP Web Services using AndroMDA” with sample project
- “REST Web Services using AndroMDA” with sample project
Modeling Dependency Injection
Dependency Injection typically used for following requirement, Simply draw a dependency from source to target UML class; AndroMDA creates a setter in the Class then IoC: Application Context initializes the object injection-
- Service => DAO Class
- Service => Service
- Service => Session Bean
- Service => Manageable Entity
- DAO Class => DAO Class
- Value Object => Entity – for transformation methods
Modeling Exception & Web Fault
Create an UML Class and apply <<ApplicationException>> stereotype or the <<UnexpectedException>> stereotype. A default exception will be generated for all services since the allowDefaultServiceException namespace property is set to true by default. A set of default CRUD exceptions will also be generated.
<<WebFault>> stereotype used for Web Service operation throwing a exception; in that cases we have model UML class with <<ApplicationException>> and <<WebFault>> stereotype.

Download’s
Sample AndroMDA model used in this article available for download. However this model may not be used directly for code generation due to dependencies.
Download: https://github.com/downloads/jeevatkm/generic-repo/sample-andromda-modeling.xml
AndroMDA UML Diagram: https://github.com/downloads/jeevatkm/generic-repo/sample-andromda-modeling.jpg
Reference: http://www.andromda.org
